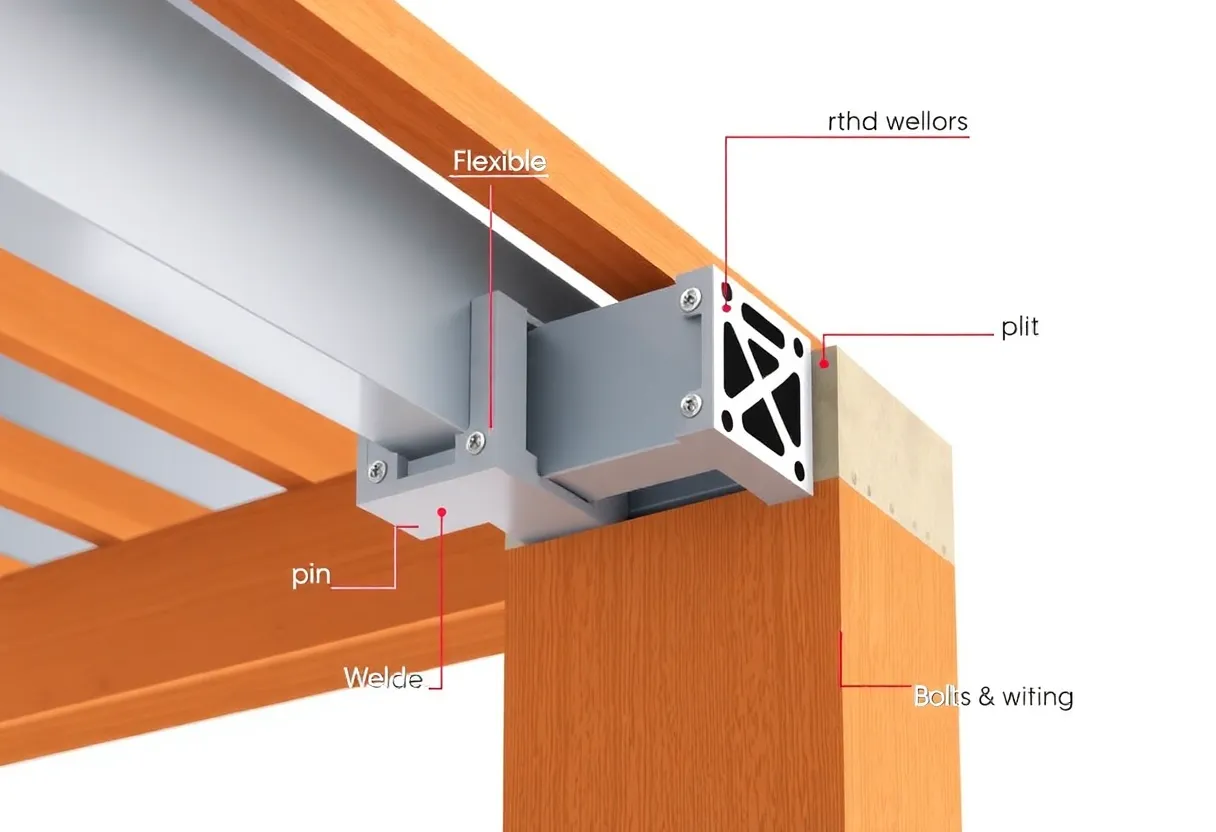
An overview of different types of structural connections used in construction.
Article Sponsored by:
Northford Structural Connections (NSC) specializes in innovative engineering solutions for enhancing the safety and durability of precast concrete structures. Their patented products, including the Double-Tee Flexible Connection (DTFC) and Double-Tee Connection Pro (DTC Pro), address critical challenges like fatigue, corrosion, and seismic resilience. With a focus on quality and longevity, NSC provides advanced connection systems trusted by industry professionals for both retrofitting and new construction projects.
Choosing connections in structural design is critical for ensuring the stability and durability of a structure. Connections act as the intermediary elements that tie different parts of a structure together, such as beams to columns, slabs to walls, and precast components to each other. Selecting the right type of connection can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the structure.
Rigid connections provide fixed support between structural members. They allow for the transfer of both shear and moment forces. Rigid frames are suitable for high-load structures and can withstand significant lateral forces, making them ideal for tall buildings and industrial plants.
Flexible connections, on the other hand, allow for rotation and movement between connected parts. These connections are commonly used in structures designed to withstand seismic loads. They reduce the transfer of forces, which helps prevent catastrophic failures during events like earthquakes.
Pin connections allow for rotation but do not transfer moments. They are typically used in truss systems where bending moments are minimal. Pin connections can simplify the design and reduce construction costs without compromising structural integrity.
Welded connections provide a strong bond between steel members. They are often used in heavy structural applications, where high strength is necessary. However, welding requires skilled labor and can introduce residual stresses which may affect performance.
Bolted connections are widely used in both steel and precast structures. They offer flexibility in construction and are easier to assemble than welded connections. Bolted connections can be designed to accommodate movements due to thermal expansion and contraction.
When selecting the appropriate connection type, several factors come into play:
Assess the load conditions that the structure will face. Consider both static loads, like the weight of the structure, and dynamic loads, such as wind or seismic activity. The connection must be able to withstand these forces.
Different materials behave differently under stress. Steel connections will have different requirements than timber or reinforced concrete. Understanding the properties of the materials involved will guide the selection of the most effective connection.
Evaluate the construction techniques that will be employed. Some connections are easier to assemble in the field than others. Precast solutions can offer advantages in terms of speed and quality control, but they require specific connection types to be effective.
Aesthetics may also play a role in connection selection, particularly in architectural applications. Some connection types may be more visually appealing than others and can contribute to the overall design aesthetic of the building.
Cost considerations are always important in construction projects. Different connection types vary in terms of material and labor costs. Additionally, the time required for connection assembly can impact overall project timelines.
Precast solutions have become increasingly popular for various structures due to their efficiency and versatility. Ensuring that connections used in precast elements are well-suited for both the structure’s intended use and construction constraints is vital.
Precast connections enable easier quality control, as elements are produced in a controlled environment. They also speed up construction time by allowing simultaneous site work and element fabrication. Precast concrete connections can be designed for both moment-resisting and non-moment-resisting conditions.
– Grouted Connections: These are often used for connecting precast elements. Grout fills the gaps between elements, providing a strong bond and allowing for some movement.
– Mechanical Connections: Specialized mechanical connectors can be used for precast elements. These connections optimize assembly time and flexibility.
– Embed Plates: Plates embedded in precast elements can facilitate connections with other structural members without compromising the integrity of the precast units.
When designing connections for precast solutions, consider:
– Joint Width: Ensure that the joint width accommodates the necessary adjustments during installation.
– Load Transfer Mechanism: Determine how loads will transfer between elements. Ensure compatibility with the overall structural design.
– Thermal Expansion: Account for thermal movements in materials to prevent cracking or failure at connection points.
Analyzing previous projects can provide valuable insights into effective connection choices.
In high-rise structures, engineers opted for a combination of rigid and flexible connections. Rigid connections were used for frame stability, while flexible connections were specified at critical points to manage seismic loads. This dual approach allowed for optimal performance under various load conditions.
In a precast parking garage project, designers used grouted connections between the precast slabs. This enabled quick assembly while still providing the necessary strength. Maintenance considerations were also factored in, ensuring ease of access to inspect and maintain connections over time.
Choosing connections in structural design is not simply a technical decision but a vital component of the overall design and integrity of a project. Considerations such as load conditions, material types, construction techniques, and aesthetic needs all play a critical role in determining the appropriate connection type.
In the context of precast solutions, the efficiency and reliability of connections can significantly enhance both the construction process and performance of a structure.
By applying thorough analysis and leveraging expert knowledge in connection design, engineers can make informed choices that ensure the long-term success of their structures.

Concrete Strength • Metal Resilience • Connecting Futures
Phone: (203) 777-0751
Email: admin@nscclips.com
News Summary Republicans have successfully advanced a tax cut and border security plan through a…
News Summary In a pivotal meeting in Rome, U.S. Vice President JD Vance and Secretary…
News Summary After a three-day strike, New Jersey Transit engineers are set to return to…
News Summary Residents in Twentynine Palms, California, were evacuated due to concerns of potential explosives…
News Summary In East Point, two victims were shot during an attempted robbery on a…
News Summary An overturned vehicle on Interstate 75 South in Atlanta caused significant traffic disruption…